In this article, I will show you how to use the ggplot2 plotting library in R. It was written by Hadley Wickham. If you don’t have already have it, install it and load it up:
install.packages('ggplot2')
library(ggplot2)
Copy
qplot
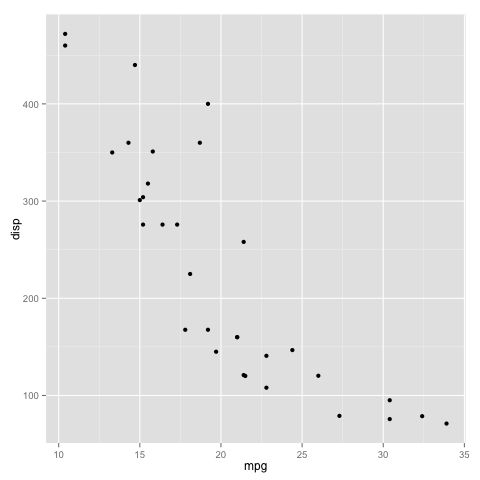
qplot is the quickest way to get off the ground running. For this demonstration, we will use the mtcars dataset from the datasets package.
library(datasets) qplot(mpg, disp, data = mtcars)Copy
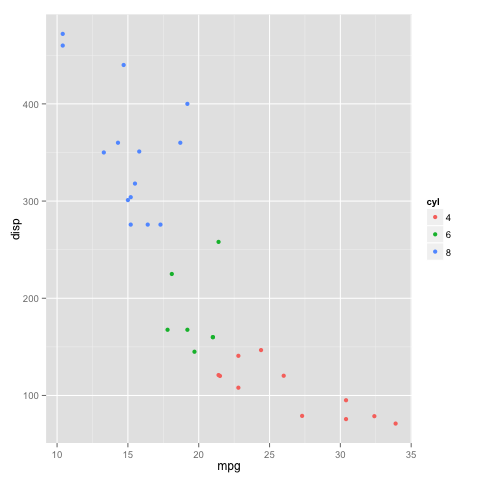
We can also color the datapoints based on the number of cylinders that each car has as follows:
mtcars$cyl <- as.factor(mtcars$cyl) qplot(mpg, disp, data = mtcars, color = cyl)Copy
which will give the following plot:
You can also plot a histogram:
qplot(mtcars$mpg, fill = mtcars$cyl, binwidth = 2) Copy
which will give the following plot:
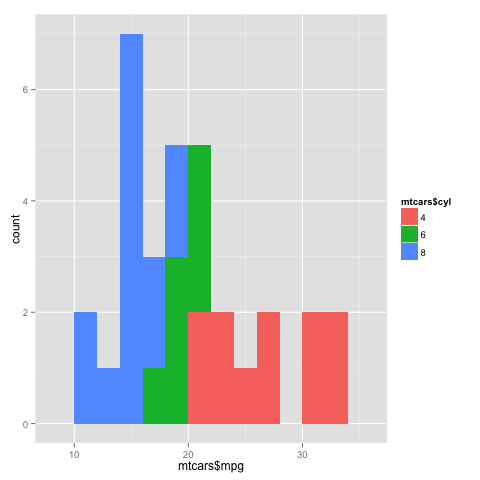
Another thing you may notice is that instead of specifying data = mtcars, I just used mtcars$mpg and mtcars$cyl here. Both are acceptable ways, and you are free to use whichever you prefer.
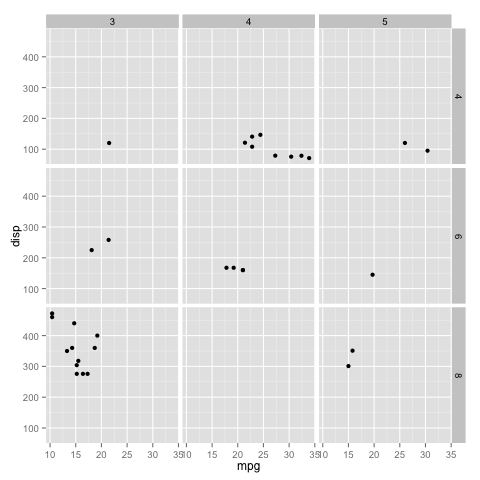
You can also split the plot using facets.
qplot(mpg, disp, data = mtcars, facets = cyl ~ .) Copy
which gives the following plot:

You can also split along both the x axes and y axes as follows:
mtcars$gear <- as.factor(mtcars$gear) qplot(mpg, disp, data - mtcars, facets = cyl ~ gear) Copy
ggplot
While qplot is a great way to get off the ground running, it does not provide the same level of customization as ggplot. All the above plots can be reproduced using ggplot as follows:
ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp)) + geom_point() ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp)) + geom_point(aes(color = cyl)) ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg)) + geom_bar(aes(fill = cyl), binwidth = 2) ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp)) + geom_point() + facet_grid(cyl ~ .) ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp)) + geom_point() + facet_grid(cyl ~ gear) Copy
Customization
There are a variety of options available for customization. I will describe a few here.
For example, for the points, we can specify size, color and alpha. Alpha determines how opaque each point is, with 0 being the lowest, and 1 being the highest value it can take.
We can specify the labels for the x axis and y axis using xlab and ylab respectively, and the title using ggtitle.
There are a variety of options for modifying the legend title, text, colors, order, position, etc.
You can also select a theme for the plot. Use ?ggtheme to see all the options that are available.
Here is an example:
ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, disp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = carb), size = 2.5, alpha = 0.8) +
facet_grid(cyl ~ gear) +
xlab('Miles per US gallon') +
ylab('Displacement in cubic inches') +
ggtitle('Fuel consumption vs displacement') +
theme(legend.background = element_rect(color = 'orange', fill = 'purple', size = 1.2, linetype = 'dotted'), legend.key = element_rect(fill = 'pink'), legend.position = 'top')
Copy
which gives the following plot:
The above plot is only for demonstration purposes, and it shows some of the many customization options available in the ggplot2 library. For more options, please refer to the ggplot2 documentation.
If you have any questions, please feel free to leave a comment or reach out to me on Twitter.